The insemination success is influenced by a lot of different factors
inside a farm:
配种工作是否卓有成效受到诸多因素的影响;
♦ Health status (PRRS, Leptospirosis,…)
猪只健康状况(蓝耳病、钩端螺旋体病……)
♦ Feeding
饲喂营养
♦ Housing */ climate
猪舍设置/舍内气候环境
^Fertility also depends to a large extent on thelighting regime. The use of instance light bands showed an increase of 0.55 inthe number of piglets born alive per sow and year.
繁殖力在很大程度上受光照制度的影响。比如,适宜的光照 能让每头母猪年产活仔数增加0.55头。
inside a farm:
配种工作是否卓有成效受到诸多因素的影响;
♦ Health status (PRRS, Leptospirosis,…)
猪只健康状况(蓝耳病、钩端螺旋体病……)
♦ Feeding
饲喂营养
♦ Housing */ climate
猪舍设置/舍内气候环境
^Fertility also depends to a large extent on thelighting regime. The use of instance light bands showed an increase of 0.55 inthe number of piglets born alive per sow and year.
繁殖力在很大程度上受光照制度的影响。比如,适宜的光照 能让每头母猪年产活仔数增加0.55头。

Figue 5:Example of a functioning light programme in mating house (Source: GFC; 2018)
You need: 1 fluorescentlamp for 2 - 3 pens, 58Watt; 1,5 m above the sow's eyes, ca. 300 Lux
需要采取措施;® 2-3个栏位安装一盏58瓦荧光灯;设置 在母猪眼睛正上方1.5米处,约300Lux。
The skills and technical professionalism of the workers are the keyfactors for the success of insemination
配种是否卓有成效的关键因素取决于操作人员的技术水平。
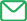
5.1Optimal timing for insemination 最佳配种时间
♦ 2 times a day heat control with an active boar - write down the result in aheat calendar.
每天两次用公猪试情,并将结果录入发情日历。
♦ Ovulation: 30 to 36 h after toleration of theboar - start of thelast third of the heat.
排卵时刻:开始静立(接受爬跨)后30 - 36 小时,即发情后三 分之一时段开始时。
♦ Difference in heat duration depends on the start of the heat: early,normal, late (24 up to 72 h).
发情持续时间的长短取决于开始发情的时间;早、正常、晚 (24 -72小 时)。
♦ Short time period for fertilisation ability of sperms (max. 24 h) andovum (ca. 4 h) in the genital tract.
精子和卵子在生殖道中保持授精能力的持续时间较短,精子最长24小时,卵子约4小时。
♦ Optimal: 16 to 24 h before and up to 4 hafter ovulation.
最佳配种时间在排卵前16-24小时至排卵后4小时。
♦ Inside a farm we are not able to detect the exact time of ovulation, sowe work with double inseminations.
因在猪场内无法精确地检测排卵时间,因而我们通常配种两次。
♦ The ovulation is mostly after 75 % of the heatperiod, or on average 42 h after the start of the heat. But there aredifferences between gilts and sows, i.e. gilts have a shorter heat period.Differences of heat duration can also be found between farms.
排卵大多数发生在发情期间的后四分之一时段,或平均在发 情42小时前后。但是和经产母猪相比,后备母猪的发情持续时间较短。不同养殖场的母猪发情持续时间也不同。
♦ A.I. after the ovulation reduces the success to achieve early gestation.
在排卵后进行人工授精会降低受胎成功率,导致母猪不能尽快妊娠。
♦ Early gestation is also influenced by breed,parity and nutritional status.
除此之外,品种、胎次以及饲喂营养效果也会影响母猪是否能够尽快妊娠。
5.2 Insemination Monitoring 配种监测
♦ For a good insemination monitoring of the chosen date of insemination ananalysis of farrowing rate, number of born piglets, live-born piglets, deadpiglets etc. should be carried out and the results should be compared fordifferent dates of insemination.
想要获得良好的配种监测效果,一定要分析各个配种环节的 关键数据,如分娩率、岀生仔猪数、活仔数、死胎数等。还要在 不同的配种批次之间横向比较这些数据结果。
♦ The observations have to be written down very carefully.
同时,各项监测结果必须认真记录。
♦ The insemination monitoring should be done for gilts and sows. It ismore than only fertility monitoring.
对后备和经产母猪都要进行配种监测,并有效利用这些监测 结果和数据,以便优化生产。
♦ The heat detection is noted two times a day beginning with day 3 after weaning.
从断奶后第3天开始,每天进行两次发情鉴定,识别发情并 予以记录。
♦ Write down the date and time of first, second and third A.I.
记录下第一次、第二次及第三次配种的日期和时间。
0Add after 21 or 28 days the results of anultrasound pregnancy test.
记录下配种后21 或 28天后的妊检结果。
♦ Add the results of farrowing (yes / no - why not; total bornpiglets, live-born piglets, dead piglets).
记录下分娩结果(分娩/没有分娩(原因)、出生仔猪数、 活产仔猪数、死胎数)。
Piglet index仔猪指数:
It is a quick and easy tool to control your reproduction success bymultiplying the farrowing rate and live-born piglets. Changes in both traits can be seen very easily.
仔猪指数是一种有效和易于掌握的母猪繁殖性能的测量方 法,通过分娩率和活产仔数计算而来,这两个参数的变化易于辨 识。
For example 例如:
♦ 84,0 x 11,7 =983 live-bornpiglets / 100 inseminatedsows
84.0 (分娩率)x 11.7 (活产仔数)=983活仔数/ 100头 配种母猪
♦ 86,0 x 12,0 = 1032 live-bornpiglets / 100 inseminatedsows
86.0 (分娩率)x 12.0(活产仔数)=1032活仔数/ 100 头配种母猪
->+ 49 live-bornpiglets with the same work!
在完成相同的工作的情况下,增加了49头活产仔猪!
You need: 1 fluorescentlamp for 2 - 3 pens, 58Watt; 1,5 m above the sow's eyes, ca. 300 Lux
需要采取措施;® 2-3个栏位安装一盏58瓦荧光灯;设置 在母猪眼睛正上方1.5米处,约300Lux。
The skills and technical professionalism of the workers are the keyfactors for the success of insemination
配种是否卓有成效的关键因素取决于操作人员的技术水平。
5.1Optimal timing for insemination 最佳配种时间
♦ 2 times a day heat control with an active boar - write down the result in aheat calendar.
每天两次用公猪试情,并将结果录入发情日历。
♦ Ovulation: 30 to 36 h after toleration of theboar - start of thelast third of the heat.
排卵时刻:开始静立(接受爬跨)后30 - 36 小时,即发情后三 分之一时段开始时。
♦ Difference in heat duration depends on the start of the heat: early,normal, late (24 up to 72 h).
发情持续时间的长短取决于开始发情的时间;早、正常、晚 (24 -72小 时)。
♦ Short time period for fertilisation ability of sperms (max. 24 h) andovum (ca. 4 h) in the genital tract.
精子和卵子在生殖道中保持授精能力的持续时间较短,精子最长24小时,卵子约4小时。
♦ Optimal: 16 to 24 h before and up to 4 hafter ovulation.
最佳配种时间在排卵前16-24小时至排卵后4小时。
♦ Inside a farm we are not able to detect the exact time of ovulation, sowe work with double inseminations.
因在猪场内无法精确地检测排卵时间,因而我们通常配种两次。
♦ The ovulation is mostly after 75 % of the heatperiod, or on average 42 h after the start of the heat. But there aredifferences between gilts and sows, i.e. gilts have a shorter heat period.Differences of heat duration can also be found between farms.
排卵大多数发生在发情期间的后四分之一时段,或平均在发 情42小时前后。但是和经产母猪相比,后备母猪的发情持续时间较短。不同养殖场的母猪发情持续时间也不同。
♦ A.I. after the ovulation reduces the success to achieve early gestation.
在排卵后进行人工授精会降低受胎成功率,导致母猪不能尽快妊娠。
♦ Early gestation is also influenced by breed,parity and nutritional status.
除此之外,品种、胎次以及饲喂营养效果也会影响母猪是否能够尽快妊娠。
5.2 Insemination Monitoring 配种监测
♦ For a good insemination monitoring of the chosen date of insemination ananalysis of farrowing rate, number of born piglets, live-born piglets, deadpiglets etc. should be carried out and the results should be compared fordifferent dates of insemination.
想要获得良好的配种监测效果,一定要分析各个配种环节的 关键数据,如分娩率、岀生仔猪数、活仔数、死胎数等。还要在 不同的配种批次之间横向比较这些数据结果。
♦ The observations have to be written down very carefully.
同时,各项监测结果必须认真记录。
♦ The insemination monitoring should be done for gilts and sows. It ismore than only fertility monitoring.
对后备和经产母猪都要进行配种监测,并有效利用这些监测 结果和数据,以便优化生产。
♦ The heat detection is noted two times a day beginning with day 3 after weaning.
从断奶后第3天开始,每天进行两次发情鉴定,识别发情并 予以记录。
♦ Write down the date and time of first, second and third A.I.
记录下第一次、第二次及第三次配种的日期和时间。
0Add after 21 or 28 days the results of anultrasound pregnancy test.
记录下配种后21 或 28天后的妊检结果。
♦ Add the results of farrowing (yes / no - why not; total bornpiglets, live-born piglets, dead piglets).
记录下分娩结果(分娩/没有分娩(原因)、出生仔猪数、 活产仔猪数、死胎数)。
Piglet index仔猪指数:
It is a quick and easy tool to control your reproduction success bymultiplying the farrowing rate and live-born piglets. Changes in both traits can be seen very easily.
仔猪指数是一种有效和易于掌握的母猪繁殖性能的测量方 法,通过分娩率和活产仔数计算而来,这两个参数的变化易于辨 识。
For example 例如:
♦ 84,0 x 11,7 =983 live-bornpiglets / 100 inseminatedsows
84.0 (分娩率)x 11.7 (活产仔数)=983活仔数/ 100头 配种母猪
♦ 86,0 x 12,0 = 1032 live-bornpiglets / 100 inseminatedsows
86.0 (分娩率)x 12.0(活产仔数)=1032活仔数/ 100 头配种母猪
->+ 49 live-bornpiglets with the same work!
在完成相同的工作的情况下,增加了49头活产仔猪!

6:配种监测(来源;德国农场咨询有限责任公司2018)
With a complete insemination monitoring you areable to find problems in the A.I. management. It is also helpful to work withthe piglet index. By this, you are able to improve the performance of theinsemination in a stepwise manner.
通过落实完整的配种监测,可及时发现配种管理中存在的问题并予以解决。仔猪指数是很有帮助的测量方法。如能贯彻落 实这些措施,将逐步获得更多的配种成果。
5.3 Artificial Insemination - step by step 人工授精操作步骤
♦ Before inseminating the sows, clean your hands thoroughly, put on newgloves and use a paper towel to clean the vulva.
在绐母猪配种之前,请彻底清洁双手,带上新手套并用纸巾 清洁外阴。
♦ Lubricate the tip of the catheter using any non-spermicidal lubricant ora few drops of extended semen. Avoid getting lubricant in the opening of thecatheter.
使用不杀精子的润滑剂或几滴精液绐输精管端口润滑,但要避 免润滑剂渗进端口。
♦ Gently guide the catheter, with the tip pointed up to avoid getting incontact with the bladder of the sow, through the vagina to the cervix.
轻慢斜上插入输精管,避免输精管接触膀胱,通过阴道抵至 子宫颈。
♦ Clean your hands and use new materials for each sow
清洁双手,每头母猪都要使用新的耗材,耗材不能重复使用
With a complete insemination monitoring you areable to find problems in the A.I. management. It is also helpful to work withthe piglet index. By this, you are able to improve the performance of theinsemination in a stepwise manner.
通过落实完整的配种监测,可及时发现配种管理中存在的问题并予以解决。仔猪指数是很有帮助的测量方法。如能贯彻落 实这些措施,将逐步获得更多的配种成果。
5.3 Artificial Insemination - step by step 人工授精操作步骤
♦ Before inseminating the sows, clean your hands thoroughly, put on newgloves and use a paper towel to clean the vulva.
在绐母猪配种之前,请彻底清洁双手,带上新手套并用纸巾 清洁外阴。
♦ Lubricate the tip of the catheter using any non-spermicidal lubricant ora few drops of extended semen. Avoid getting lubricant in the opening of thecatheter.
使用不杀精子的润滑剂或几滴精液绐输精管端口润滑,但要避 免润滑剂渗进端口。
♦ Gently guide the catheter, with the tip pointed up to avoid getting incontact with the bladder of the sow, through the vagina to the cervix.
轻慢斜上插入输精管,避免输精管接触膀胱,通过阴道抵至 子宫颈。
♦ Clean your hands and use new materials for each sow
清洁双手,每头母猪都要使用新的耗材,耗材不能重复使用

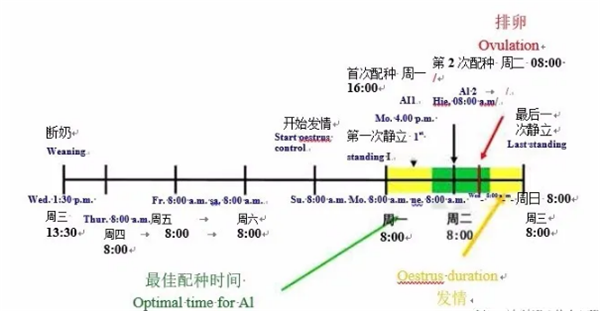
Figure 7: Putting thecatheter into the sow's vulva
图7;将输精管插入母猪外阴
♦ A foam-tipped catheter isinserted up against the cervix:
将输精管(带泡沫端头)插入子宫颈;
Figure 8: Pushing the catheter up to the cervix(Source: GFC; 2018)
匿8:将输精管斜上推至子宫颈(来源;德国农场咨询有限 责任公司2018)
♦ Gently invert the bottle of diluted semen two or three times to mix thesemen.
轻轻地将装盛已稀释精液的精液袋倒置,并摇晃2到3次来 混合精液。
♦ Attach the bottle to the end of the catheter and discharge the semenslowly.
将精液袋与输精管末端连接,使精液缓慢流岀。
♦ A gentle squeeze to start the process may be needed, but after that thesemen should be allowed to be taken up by the sow (uterine contractions).
可能需要起先轻轻的挤圧精液袋,但之后要让精液自行流岀 (通过母猪子宫收缩)。
♦ This process takes at least 3 minutes.
整个输精过程至少需要3分钟。
♦ Gilts often take longer for insemination than breeding sows.
后备母猪(即头胎母猪)需要的输精时间比经产母猪略长。
♦ Depositing the semen too rapidly will cause a backflow of semen out ofthe vulva.
流注得太快会导致精液倒流岀阴户
— In naturalservice, the boar spends 5 to 10 minutes at each breeding.
-一般本交时,公猪每次输精需要5 到 10分钟
♦ A small amount of semen backflow is expected. If a big amount ofbackflow occurs, stop the insemination.
会有少量精液倒流,如果发生大量倒流,则要停止输精
♦ If semen flow stops
如果精液停止流动
♦ turn or move the catheter back and forward a bit to reinitiate semenflow.
稍微向前或向后移动或转动输精管,让精液重新开始流动
♦ cut a small hole in the semen bottle if flow has stopped because of avacuum inside the bottle.
由于精液袋内的真空现象导致流动停止,则可以在袋上扎出 一个小孔
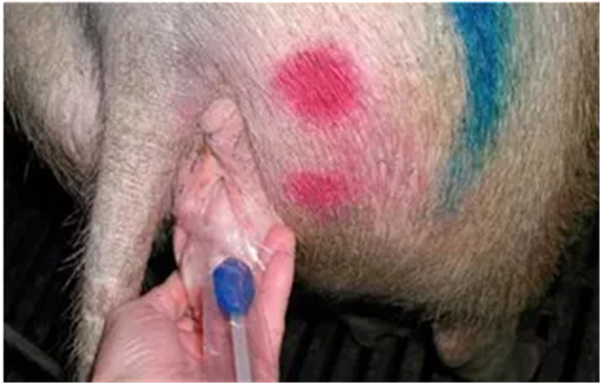
图7;将输精管插入母猪外阴
♦ A foam-tipped catheter isinserted up against the cervix:
将输精管(带泡沫端头)插入子宫颈;
Figure 8: Pushing the catheter up to the cervix(Source: GFC; 2018)
匿8:将输精管斜上推至子宫颈(来源;德国农场咨询有限 责任公司2018)
♦ Gently invert the bottle of diluted semen two or three times to mix thesemen.
轻轻地将装盛已稀释精液的精液袋倒置,并摇晃2到3次来 混合精液。
♦ Attach the bottle to the end of the catheter and discharge the semenslowly.
将精液袋与输精管末端连接,使精液缓慢流岀。
♦ A gentle squeeze to start the process may be needed, but after that thesemen should be allowed to be taken up by the sow (uterine contractions).
可能需要起先轻轻的挤圧精液袋,但之后要让精液自行流岀 (通过母猪子宫收缩)。
♦ This process takes at least 3 minutes.
整个输精过程至少需要3分钟。
♦ Gilts often take longer for insemination than breeding sows.
后备母猪(即头胎母猪)需要的输精时间比经产母猪略长。
♦ Depositing the semen too rapidly will cause a backflow of semen out ofthe vulva.
流注得太快会导致精液倒流岀阴户
— In naturalservice, the boar spends 5 to 10 minutes at each breeding.
-一般本交时,公猪每次输精需要5 到 10分钟
♦ A small amount of semen backflow is expected. If a big amount ofbackflow occurs, stop the insemination.
会有少量精液倒流,如果发生大量倒流,则要停止输精
♦ If semen flow stops
如果精液停止流动
♦ turn or move the catheter back and forward a bit to reinitiate semenflow.
稍微向前或向后移动或转动输精管,让精液重新开始流动
♦ cut a small hole in the semen bottle if flow has stopped because of avacuum inside the bottle.
由于精液袋内的真空现象导致流动停止,则可以在袋上扎出 一个小孔

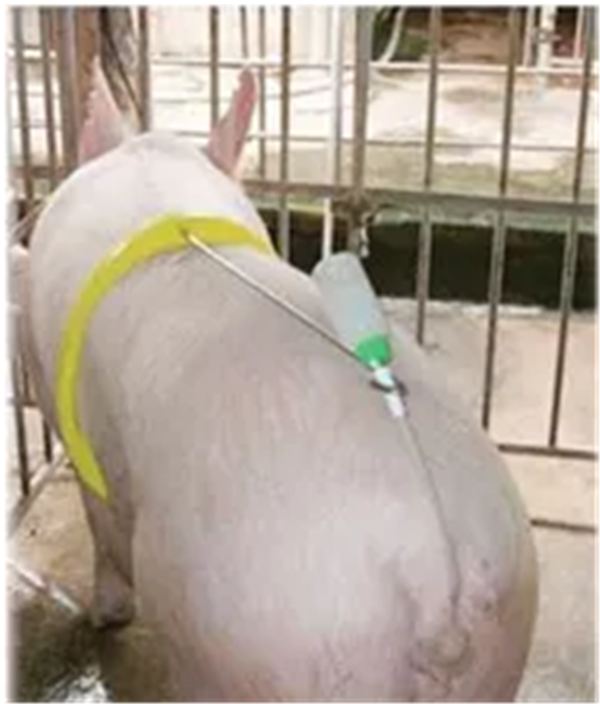
Figure 9: Usage of boar imitating materials (Source: www.landwirt.com,2019
9:使用模仿公猪爬跨的工具(来源:com 2019)
♦ If there is a great deal ofresistance to the flow of semen, reposition the catheter because the tip may belodged against a cervical fold.
如果精液流动遇有阻力,需挪移输精管,因其端口可能已紧 贴子宫颈褶皱
♦ Semen transport and fertilization can be inefficient when females arefrightened or disturbed. Females should always be handled calmly and gently.The breeder is trying to mimic the boar, and the breeder who takes the extratime and effort to imitate this well will have more success with A.I.
当母猪受到惊吓或侵扰时,精液的输送和受精效果会受到影 响,因而配种时对待母猪应始终采取平静和温和的方式。为了达 到更好的配种效果,配种员应花额外的时间和精力尝试模仿公猪。
♦A boar should always be present in front of thesows.
常规输精时应确保公猪始终出现在母猪面前
♦ Apply back-pressure to the sow in the presence of the boar and massagethe female's flank during insemination to increase the number or intensity ofuterine contractions that transport semen into the uterus.
对母猪压背,并在输精过程中按摩母猪侧腹,以增加子宫收 缩的次数和强度。
♦ If a sow refuses the boar, simply remove it for at least an hour andthen try again.
如果母猪表现岀对公猪的拒绝,则需要将公猪转离至少一小 时,之后再次尝试。
♦ Sows have to initiate uterine contractions for sperm transport with thestanding reflex.
母猪必须通过静立反射让子宫收缩,以便完成精液输送。

9:使用模仿公猪爬跨的工具(来源:com 2019)
♦ If there is a great deal ofresistance to the flow of semen, reposition the catheter because the tip may belodged against a cervical fold.
如果精液流动遇有阻力,需挪移输精管,因其端口可能已紧 贴子宫颈褶皱
♦ Semen transport and fertilization can be inefficient when females arefrightened or disturbed. Females should always be handled calmly and gently.The breeder is trying to mimic the boar, and the breeder who takes the extratime and effort to imitate this well will have more success with A.I.
当母猪受到惊吓或侵扰时,精液的输送和受精效果会受到影 响,因而配种时对待母猪应始终采取平静和温和的方式。为了达 到更好的配种效果,配种员应花额外的时间和精力尝试模仿公猪。
♦A boar should always be present in front of thesows.
常规输精时应确保公猪始终出现在母猪面前
♦ Apply back-pressure to the sow in the presence of the boar and massagethe female's flank during insemination to increase the number or intensity ofuterine contractions that transport semen into the uterus.
对母猪压背,并在输精过程中按摩母猪侧腹,以增加子宫收 缩的次数和强度。
♦ If a sow refuses the boar, simply remove it for at least an hour andthen try again.
如果母猪表现岀对公猪的拒绝,则需要将公猪转离至少一小 时,之后再次尝试。
♦ Sows have to initiate uterine contractions for sperm transport with thestanding reflex.
母猪必须通过静立反射让子宫收缩,以便完成精液输送。

Figure 10: Boaron the boar boulevard for stimulation of the sows (Source: GFC; 2018)
ffi 10 :在公猪通道对母猪诱情的公猪
♦ When all of the semen has been "sucked" into the uterus,remove the catheter by rotating it clockwise while gently pulling.
所有精液被子宫“吸入”后,顺时针旋转输精管并轻慢拉出。
♦ A new catheter should be used for each insemination to avoidtransmission of disease or infection from one sow to another.
每次输精均需使用新的输精管,以防母猪之间传染疫病。
♦ Keep the newly inseminated sows in quiet surroundings for 20 to 30minutes.
确保已受精配种的母猪在安静的环境中待驻20到30分钟。
—Stress could disrupt semen transport and fertilization.
—精神圧力会破坏精液的输送,影响受胎率。
♦ Write down the date and time of A.I. into the insemination monitoringlist!!!
在配种监测清单中明确记录配种的日期和时间! ! !
ffi 10 :在公猪通道对母猪诱情的公猪
♦ When all of the semen has been "sucked" into the uterus,remove the catheter by rotating it clockwise while gently pulling.
所有精液被子宫“吸入”后,顺时针旋转输精管并轻慢拉出。
♦ A new catheter should be used for each insemination to avoidtransmission of disease or infection from one sow to another.
每次输精均需使用新的输精管,以防母猪之间传染疫病。
♦ Keep the newly inseminated sows in quiet surroundings for 20 to 30minutes.
确保已受精配种的母猪在安静的环境中待驻20到30分钟。
—Stress could disrupt semen transport and fertilization.
—精神圧力会破坏精液的输送,影响受胎率。
♦ Write down the date and time of A.I. into the insemination monitoringlist!!!
在配种监测清单中明确记录配种的日期和时间! ! !